Composition of Dairy Ingredients
Understanding Composition of Dairy Ingredients
Getting to know each dairy ingredient by its composition is the first step in understanding its performance and matching the right ingredient with the target food application.
Breaking down each ingredient into the categories of Protein, Fat, Moisture, Lactose (sugar) and MineralsGenerally refers to elements other than carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) and nitrogen (N) that are found in dairy products. The term often is used interchangeably with salts and ash. (ashResidue that remains when milk/whey is heated to very high temperatures in a muffle oven. Organic acids are lost during ashing. Some minerals such as sulfur and phosphorous also may be lost. Other minerals may be converted to oxides, sulfates, phosphates, silicates and chlorides. In general, ash overestimates the concentration of minerals present since oxygen is combined with minerals in the remaining ash. The term often is used interchangeably with minerals and milk salts.), gives us a good starting point for recognizing how an ingredient could perform.
Utilize this page and the referenced compositions for dairy ingredients, and please note that any given parameter may vary from ingredient to ingredient, e.g. some are dry basis while others are as-is. Please refer to the ADPI Ingredient Standard for full details on any ingredient in question.

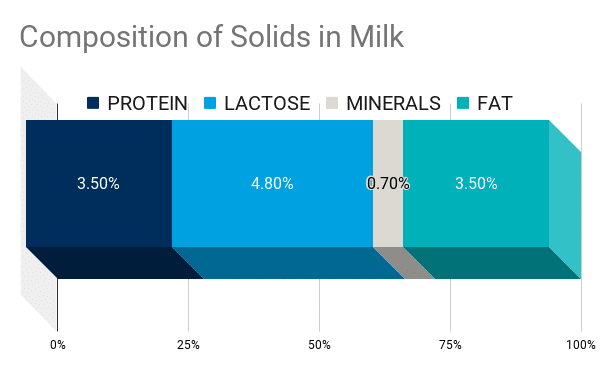
Composition of Milk
The basic building blocks of milk start with 87.5% water and 12.5% solids, making milk an extremely hydrating beverage on its own.
Once the water is removed, the 12.5% solids are broken down into protein (3.5%), lactose (4.8%), mineralsGenerally refers to elements other than carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) and nitrogen (N) that are found in dairy products. The term often is used interchangeably with salts and ash. (0.7%) and fat (3.5). Those solids contain 17 different vitamins (A, B1, B2, P,HHydrogen, KPotassium, B6, B7, B9, E, CCarbon B12, PP, B4, B3, D, B8) and 20 different mineralsGenerally refers to elements other than carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) and nitrogen (N) that are found in dairy products. The term often is used interchangeably with salts and ash. (I, KPotassium, CaCalcium, Co, MgMagnesium, J, Mn, CuCopper, Mo, Se, S, P, F, ClChloride is the anionic form of the diatomic molecule chlorine (Cl2). Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) is the active oxidizing agent that kills bacteria, viruses and fungi., ZnZinc, FeIron, Pb, Cr, Ag, Sn).
Whole milk in its purest form is measured at 3.5% fat, making it 97% fat free. Reduced, skim, and nonfat milk are produced simply by the removal of fat particles by putting whole milk into a centrifuge to separate out the fat particles.
Dried Dairy Ingredients Composition Summary
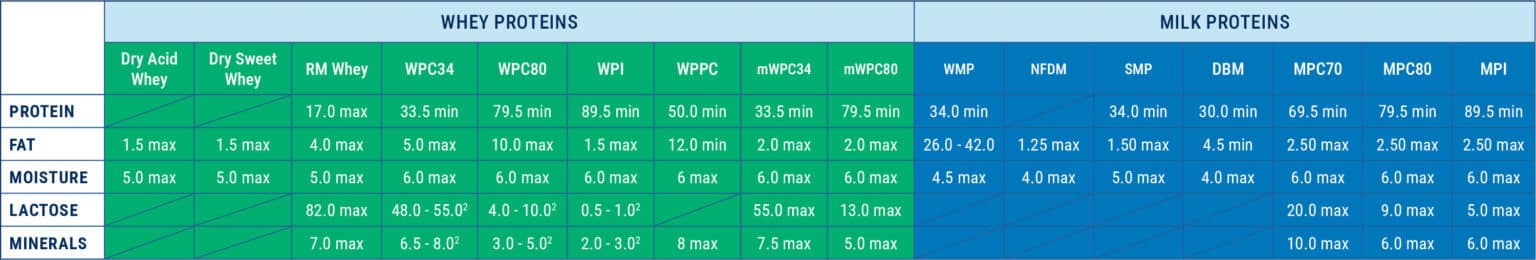
- DMB.......... Dry Buttermilk
- MPC70...... Milk Protein Concentrate 70%
- MPC80...... Milk Protein Concentrate 80%
- MPI........... Milk Protein Isolate
- mWPC34.. Milk Whey Protein Concentrate 34%
- mWPC80.. Milk Whey Protein Concentrate 80%
- NFDM....... Nonfat Dry Milk
- RM Whey.. Reduced Minerals Whey
- SMP.......... Skim Milk Powder
- WMP.......... Whole Milk Powder
- WPC34...... Whey Protein Concentrate 34%
- WPC80...... Whey Protein Concentrate 80%
- WPI........... Whey Protein Isolate
- WPPC........ Whey Protein Phospholipid Concentrate (Aslo MFGM)
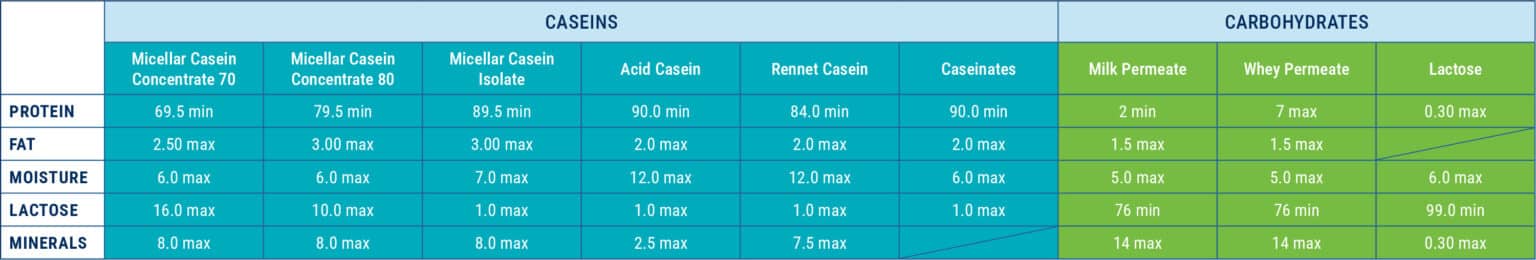
The following carbohydrates are also identified as shown below (Dairy PermeateProduced by the removal of protein and other solids from milk or whey resulting in a product with a high concentration of lactose. Removal of the dairy constituents is accomplished by physical separation techniques such as filtration and diafiltration. Also known as dairy product solids (ADPI definition). and Dairy Products Solids are acceptable for both Milk and WheyLiquid obtained from cheese manufacture. Permeate):
- Lactose................... Milk Sugar, Edible Lactose, Food Grade Lactose
- Milk Permeate ....... Dairy Permeate, Dairy Products Solids
- Whey Permeate...... Dairy Permeate, Dairy Products Solids, Deproteinized Whey, Dried Whey Product, Dried Whey Solubles