
Functionality of Dairy Ingredients
How Dairy Ingredients Perform
Whether you are seeking clean-label ingredients for high-protein applications or heat stability for a shelf-stable beverage, look to dairy ingredients to deliver functionality and nutrition with mild flavors to almost any application.
Milk and whey ingredients provide multiple benefits to food products. These benefits are often described as flavor, function, and nutrition. They provide a mild, dairy flavor that blends well with many food products. Their composition can consist of multiple components such as, proteins (caseins and/or whey proteins), milkfat, lactose, and ash (minerals), and thus provides many different functional properties as described in the table below. These components also provide many of the same unique nutritional properties found in milk.

Different Functional Properties
| Property | Definition |
|---|---|
| Hydration Rate | the rate at which particles in the powder fully absorb water (hydrate) and become surrounded by water molecules |
| Emulsification | process of combining two immiscible liquids (fat and water) to form a semi-stable mixture |
| Gelation | formation of a semi-solid network (gel) through the action of heat and/or acid |
| Water Binding | the ability of a protein or carbohydrate matrix to expand and hold onto water without solubilization |
| Viscosity | resistance of a fluid to flow or deformation under force |
| Whipping | the ability of a liquid or semi-solid to incorporate (whipability) and hold air (foam stability) after vigorous beating |
| Browning | the process of a food developing a brown color and flavor due to a chemical reaction in the presence of reducing sugar(s), amino acid(s), and water, especially with heat |
| Heat Stability | a food's ability to maintain its structure, functionality, and taste after high temperature treatment |
| Acid Stability | the ability of a food to maintain its structure, functionality, and taste in an acidic (low pH) environment |
Solubility of Dairy Ingredients
Solubility in water is the single most important functional property for a milk or whey ingredient. No matter which ingredient you choose, it must be soluble for it to be functional.
The solubility of a milk or whey ingredient that contains protein is impacted by the pH of the food. Milk protein ingredients have good solubility above pH 6.0. Whey protein ingredients have good solubility at pH 3-7. Lactose, the main component in the ingredients lactose and milk/whey permeate (dairy products solids) has good solubility below a concentration of 14% in room temperature water, but has lower solubility (will crystallize) at refrigeration temperatures. The solubility of dairy ingredients that are high in calcium (such as milk/whey permeate), decrease with heat treatment and at a pH greater than 5. These are the primary characteristics to help select the right dairy ingredient for your application.
Functional Properties of Dried Dairy Ingredients
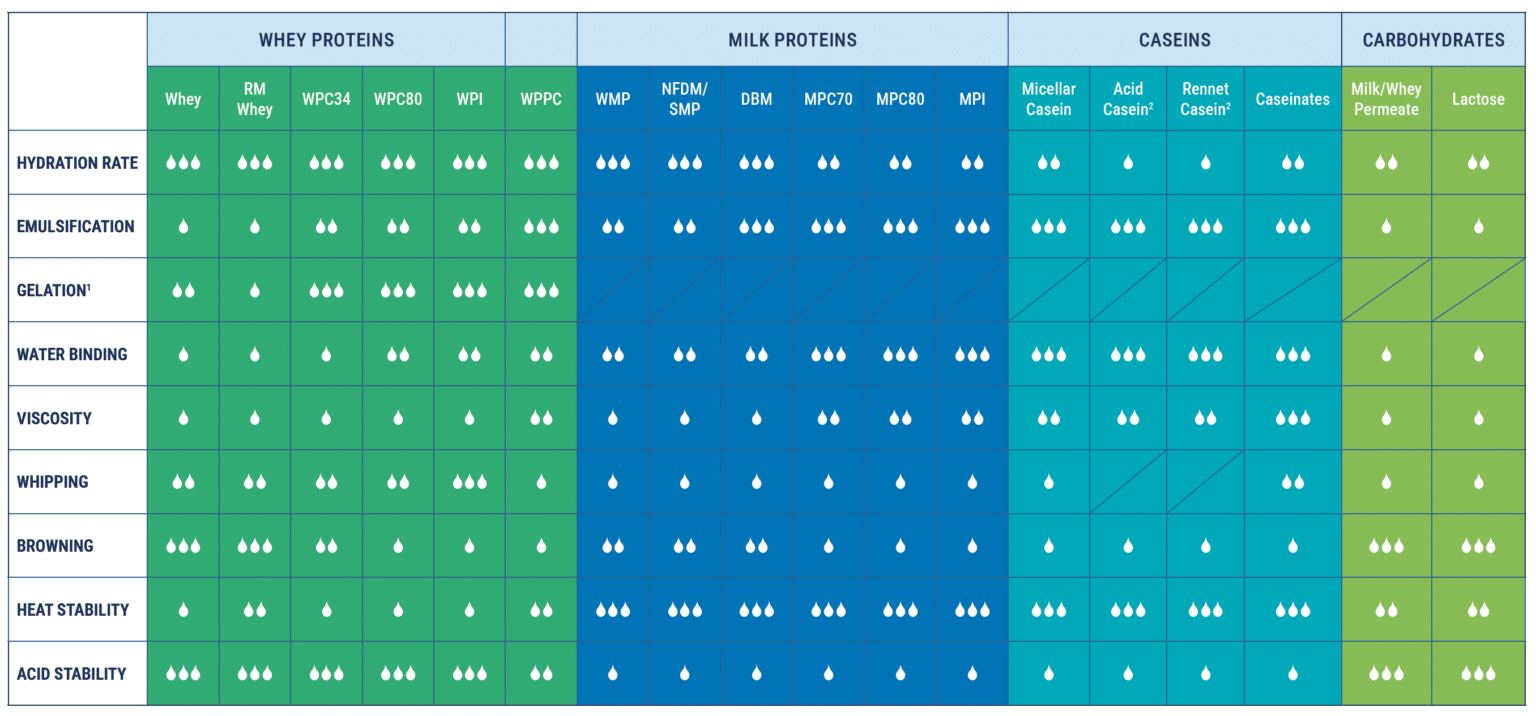

- DMB............... Dry Buttermilk
- MPC............... Milk Protein Concentrate
- MPI................ Milk Protein Isolate
- NFD/SMP...... Nonfat Dry Milk/Skimmed Milk Powder
- RM Whey...... Reduced Minerals Whey
- WMP..............Whole Milk Powder
- WPC............. Whey Protein Concentrate
- WPI...............Whey Protein Isolate
- WPPC...........Whey Protein Phospholipid Concentrate


